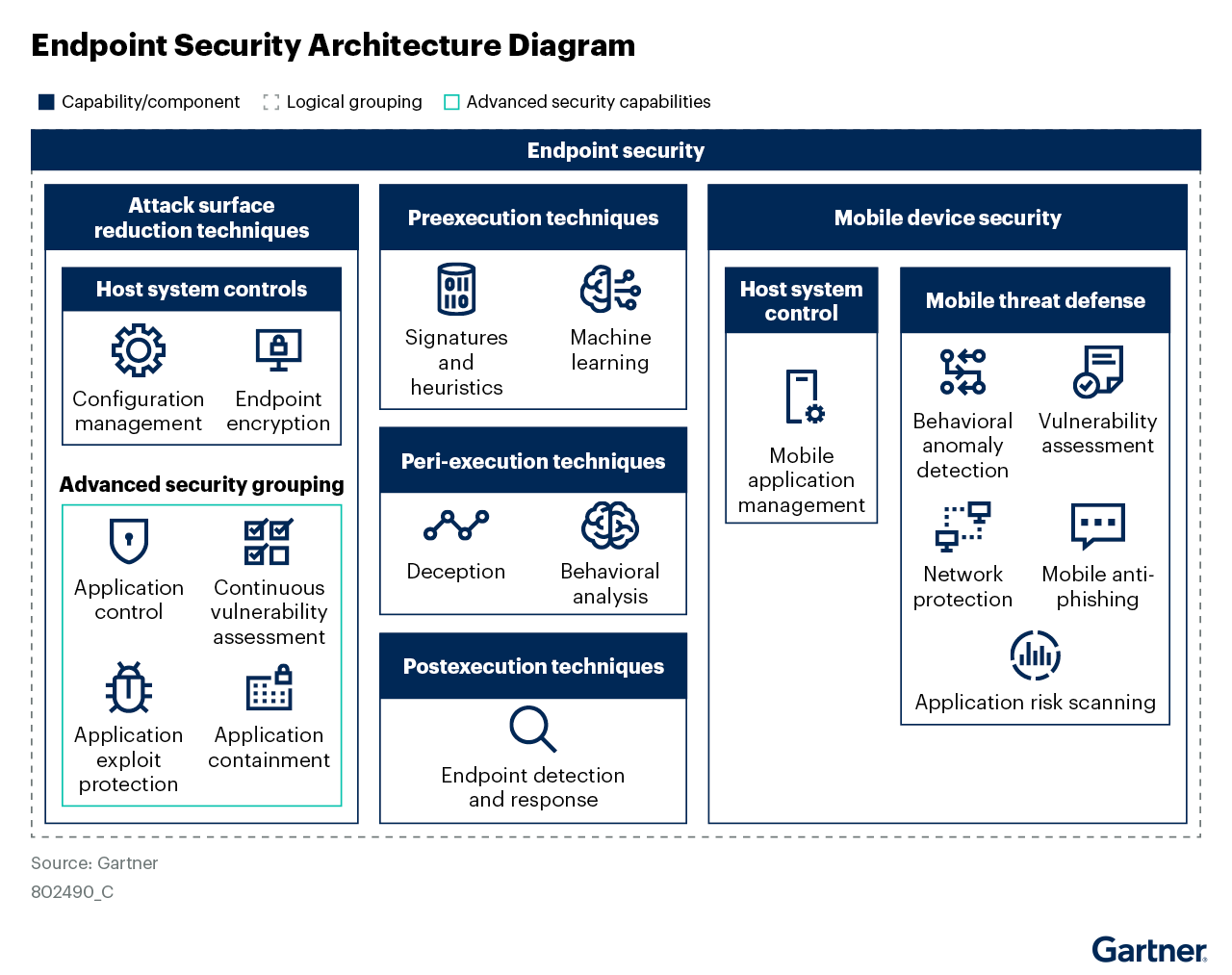
According to the 2024 Gartner® “Reference Architecture Brief: Endpoint Security report “Endpoint security is the first line of defense for the largest attack surface within any organization. This brief provides guidance for security and risk management technical professionals on what components make up the endpoint security stack and what kind of protection each component provides.”1
Figure 1: Endpoint Security Architecture Diagram
Deception technology for “peri-execution” attack detection. The endpoint security architecture (shown in Figure 1 above) describes the technologies that make up an endpoint protection platform.
It highlights deception technology as part of peri-execution techniques that are meant to block unwanted actions upon execution.
The Gartner report indicates, “ Deception deploys highly credible deceptive artifacts, such as credentials, files, or applications. The first step in the process is to deploy breadcrumbs onto the endpoint. Deceptive artifacts (created in an automated manner) are deployed into the network to deceive attackers and trap them during the early stages of the cyber kill chain”1
Acalvio’s opinion and analysis on endpoint security and the role of deception technology
Adversaries can establish an initial beachhead on any of an organization’s endpoints. Not only are they gaining in speed and stealth, but based on industry research, adversary breakout time is reducing yearly. The rapid reduction in adversary breakout time reduces the available time window for threat detection and response. Early and precise threat detection is now more essential than ever to enable response actions to isolate the threat and prevent threat propagation.
The key architectural principle is to adopt a defense-in-depth approach to cybersecurity with a layered strategy that combines prevention with detection layers.
Deception as an early threat detection layer for endpoint security
Deception serves as an important “peri-execution” detection layer, providing early threat detection for endpoint security.
Traditional forms of threat detection are suitable to detect post-exploitation actions. These approaches include log analytics, anomaly-based detection, and behavior-based detection. Traditional detection approaches are based on observing activity on real assets and identifying malicious activity by differentiating legitimate traffic from malicious or by looking for specific known behaviors indicative of malicious activity. This approach requires a certain level of signal to emerge before the activity can be classified as malicious. While each detection method has its benefits, traditional forms of detection are best suited for post-exploitation detection techniques.
Deception technology is based on fundamentally different principles that provide independent detection benefits as part of a defense-in-depth approach. Deception technology involves predicting the adversary’s actions, setting traps, and observing for interactions with the traps. Deceptions are not used in legitimate workflows, and any usage of them is an indicator of malicious activity. By using deception, organizations gain early and high-fidelity detection of a compromise, removing the need for baselining or observing attacker actions for periods of time. SOC teams also gain immediate, actionable alerts that accelerate response actions to prevent attack propagation and protect critical assets.
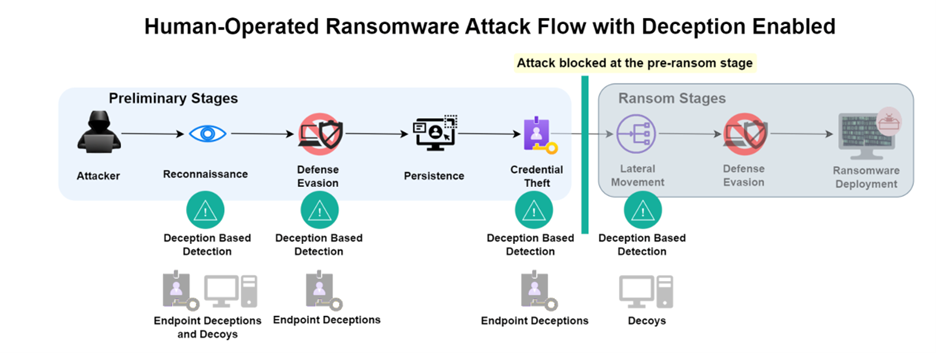
Sample attack scenario – human-operated ransomware
The typical attack scenario for a human-operated ransomware that lands on an endpoint is outlined below.
Figure 2: Ransomware Attack Flow with Deception
Deceptions enable the detection of adversarial actions at the pre-ransom stage, including detection of reconnaissance, defense evasion, credential access, and lateral movement attempts. The early and precise threat detection equips SOC teams to perform response actions to isolate the endpoint and prevent attack propagation. In the case of human-operated ransomware, deception enables the threat to be isolated before the ransomware is detonated, protecting the organization from the financial and reputational damage associated with the ransomware exploits.
Detecting threats targeting unmanaged endpoints
Organizations have a significant set of unmanaged endpoints, including IoT devices such as cameras, printers, legacy IT equipment, and endpoints running custom OS versions. These endpoints are not compatible with traditional threat detection solutions, providing opportunities for adversaries to target them and launch offensive actions from them. In addition to the absence of detection, unmanaged endpoints tend to be less frequently patched, making the prevention-based security controls less effective.
Adversaries target unmanaged endpoints, leverage offensive tooling, and launch attacks against critical assets. Recent threat research has indicated that over 25% of all attacks originate from unmanaged endpoints.
Deception technology provides a proven approach to threat detection for threats targeting unmanaged endpoints. Security teams can deploy decoys that represent unmanaged endpoints and honeytokens in identity stores to gain early detection of these threats, providing a detection layer to expand the threat detection coverage to include unmanaged endpoints for comprehensive endpoint security.
Summary
Adversaries start their offensive actions from endpoints. To prevent attack propagation, a defense-in-depth approach for endpoint security that combines prevention and detection layers is essential.
Deception technology is an essential detection layer for endpoint security. For managed endpoints, deception provides the benefit of early threat detection, detecting threats at the peri-execution stage before traditional forms of detection. Defense teams gain the ability to perform response actions to isolate the threat and protect the assets.
For unmanaged endpoints, deception enables the detection of threats targeting and originating from unmanaged endpoints, expanding threat detection coverage and providing new visibility to defense teams.
Organizations can combine deception technology with EDR for comprehensive threat detection and apply prevention-based controls for a mature endpoint security program.
For more information on ShadowPlex deception for endpoint security, schedule a demo.
1Gartner, Reference Architecture Brief: Endpoint Security, By Eric Grenier, 16 February 2024 GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.