- Products
-
ProductsPlatform
- ShadowPlex Advanced Threat Defense
Deception for early detection of cyber threats with precision and speed
- ShadowPlex Identity Protection
Visibility, management and protection of identity stores and attack paths
- Acalvio Active Defense Platform
Comprehensive and Award-winning Distributed Deception Platform
- What is Active Defense?
Active defense detects and diverts attacks.
- Why do I need Acalvio Active Defense?
Active Defense deceives and disrupts attackers.
- ShadowPlex Advanced Threat Defense
-
- Solutions
-
Technology SolutionsIndustry Solutions
- Breach Detection
Active Defense for breach detection and response, both in on-premises and cloud workloads
- Identity Threat Detection & Response
Visibility into Identity attack surface and effective detect & respond solution for identity attacks
- OT / ICS Security
Passive and low-risk agentless solution that is easy to deploy
- Active Directory Protection
Visibility into AD attack surfaces and detection of AD Attacks
- Threat Hunting
Active threat hunting, based on targeted deception, to confirm hunting hypothesis
- Ransomware
AI-Driven Advanced Deception Technology to combat even zero-day Ransomware
- Honeytokens for CrowdStrike
Honeytokens are deceptive credentials and data that are embedded in legitimate assets
- Zero Trust
Zero trust is a security model that assumes that no one inside or outside of the network can be trusted
- Public Sector
Targeted solution for protecting Federal agencies in conformation with NIST and CISA recommendations
- Healthcare
Active defense solutions thwart healthcare attacks before they can inflict real damage.
- Breach Detection
-
- Resources
- Partners
- Company
Red Teaming
What is Red Teaming?
A red teaming exercise is a proactive cybersecurity practice where a group of skilled and independent security experts, known as the “red team,” simulate real-world cyberattacks on an organization’s systems, networks, and physical infrastructure. The purpose of red teaming is to identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and gaps in an organization’s security defenses that might not be easily detectable through traditional assessments.
The red team employs various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to mimic the tactics of actual adversaries, helping organizations better understand their risk exposure and improve their overall cybersecurity posture. The insights gained from a red teaming exercise can aid in enhancing incident response plans, strengthening defenses, and refining security strategies.
How Does Red Teaming Function?
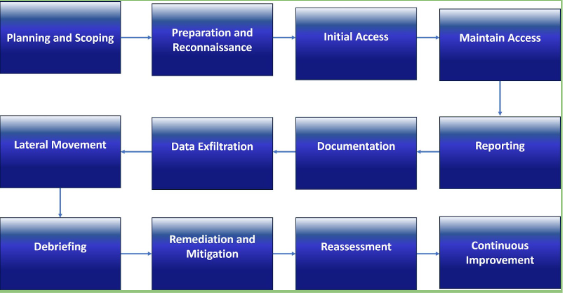
Red teaming is a structured and systematic approach to evaluating the security and effectiveness of an organization’s systems, processes, and defenses. The following are the steps involved in a red teaming process:
1. Planning and Scoping:
- Define objectives and goals.
- Determine the scope and boundaries of the exercise.
- Set rules of engagement for the red team.
2. Preparation and Reconnaissance:
- Gather information about the target organization.
- Analyze threat intelligence for realistic attack scenarios.
- Develop a detailed attack plan.
3. Initial Access:
- Attempt to gain initial access to the organization’s systems.
4. Maintaining Access:
- Establish persistence within the network.
- Create backdoors or exploit vulnerabilities.
5. Lateral Movement:
- Move laterally through the network to access other systems.
6. Data Exfiltration:
- Attempt to steal sensitive data or demonstrate the impact of a successful breach.
7. Documentation:
- Thoroughly document all actions taken during the exercise.
8. Reporting:
- Prepare a detailed report with findings, vulnerabilities, and recommendations.
9. Debriefing:
- Discuss results and lessons learned with stakeholders.
10. Remediation and Mitigation:
- Address identified vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
11. Reassessment:
- Periodically repeat the exercise to test improvements.
12. Continuous Improvement:
- Use insights to enhance security measures continuously.
- Red teaming helps organizations identify and mitigate security risks by simulating real-world attacks and evaluating their defenses and response capabilities.
What Are the Benefits of Red Teaming?
Red teaming offers several key benefits to organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture:
- By simulating real-world cyberattacks, red teaming uncovers vulnerabilities and blind spots that might otherwise go undetected, providing a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s defenses.
- This proactive approach helps organizations identify and address weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them.
- Red teaming also fosters a better understanding of potential attack vectors, helping security teams develop effective strategies for incident response and mitigation.
- Additionally, red teaming enhances collaboration and communication among cross-functional teams, improves incident detection and response capabilities, and contributes to ongoing improvements in overall security readiness.
What are the differences between Red Teaming and Penetration Testing?
Red teaming and penetration testing are both crucial cybersecurity assessments, but they differ in scope and objectives. Penetration testing, often referred to as “pen testing,” focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in specific systems or applications to assess their security posture. Pen testers aim to exploit weaknesses and provide a detailed report of vulnerabilities discovered.
In contrast, red teaming is a broader and more comprehensive exercise that simulates real-world cyberattacks. The red team attempts to emulate the tactics of adversaries across various attack vectors, including social engineering, physical security, and more. The goal of red teaming is to assess an organization’s overall resilience and readiness by identifying potential blind spots and uncovering vulnerabilities that might be missed in traditional assessments. While penetration testing dives deep into specific targets, red teaming takes a holistic approach to test an organization’s entire security ecosystem.
What are the benefits of Red Teaming?
Red teaming offers several key benefits to organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture. By simulating real-world cyberattacks, red teaming uncovers vulnerabilities and blind spots that might otherwise go undetected, providing a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s defenses. This proactive approach helps organizations identify and address weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them. Red teaming also fosters a better understanding of potential attack vectors, helping security teams develop effective strategies for incident response and mitigation. Additionally, red teaming enhances collaboration and communication among cross-functional teams, improves incident detection and response capabilities, and contributes to ongoing improvements in overall security readiness.
How can cyber deception help in Red Teaming?
Cyber deception plays a valuable role in red teaming exercises by adding a layer of realism and complexity to the assessment. By deploying deceptive elements like decoys, lures, baits, breadcrumbs, and false information, cyber deception provides the red team with dynamic scenarios that mimic actual attack situations. This challenges the red team to adapt their tactics and techniques, closely simulating the unpredictable nature of real-world adversaries.
The inclusion of cyber deception in red teaming enhances the exercise’s effectiveness by testing not only an organization’s technical defenses but also the ability of its security teams to detect, respond, and adapt to evolving threats in a dynamic environment.